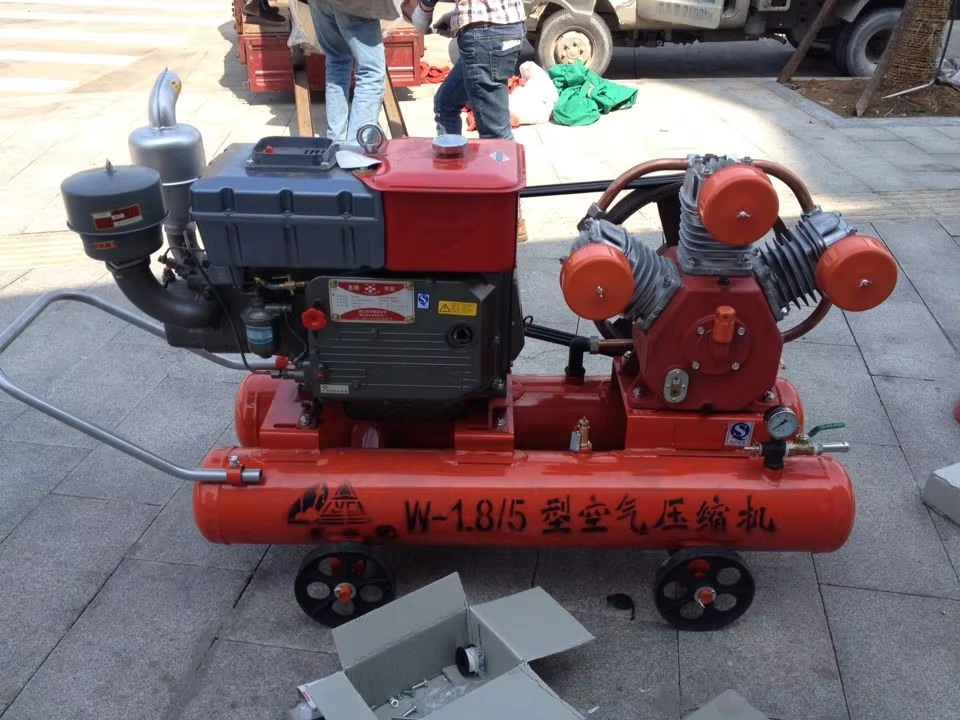
Airflow and Pressure Performance: CFM, PSI, and Real-World Application Matching

Understanding CFM and PSI in Diesel Air Compressor Output
Industrial diesel air compressors need just the right mix of airflow (CFM) and pressure (PSI) to get the job done properly. The CFM basically tells us how much air is moving through the system each minute, whereas PSI shows us how hard that air is pushing against whatever it's powering. There's this interesting thing called Boyle's Law at work here too. When we crank up the pressure (PSI), guess what happens? We actually end up with less airflow (CFM). Take a standard unit rated for 100 CFM at 100 PSI as an example. If it gets really hot out or super cold in winter conditions, that same compressor might drop down by around 2 to 3 percent in terms of efficiency. Getting these two numbers balanced correctly matters a lot because otherwise we're wasting fuel money and our pneumatic tools like those heavy duty jackhammers and sand blasting equipment won't operate as intended when workers need them most.
Free Air Delivery (FAD) and Its Impact on Real-World Performance
The Free Air Delivery (FAD) measurement shows what an air compressor actually delivers once we factor in all those losses from heat, friction inside the machine, and other internal inefficiencies. Theoretical CFM ratings don't tell the whole story here. For example, if a compressor claims 25 cubic feet per minute (CFM), it might realistically only produce between 18 to maybe 22 FAD because diesel engines just aren't perfectly efficient when it comes to converting fuel into compressed air. This difference really matters for equipment running nonstop day after day since what actually comes out determines how productive workers can be. Up in mountainous areas where miners operate their heavy machinery, adding at least a 15 percent extra cushion to FAD capacity makes sense as thinner air at higher elevations naturally reduces engine performance anyway.
Matching Airflow to Application Demands
Different tools require specific airflow and pressure:
- Pneumatic drills: 30–40 CFM @ 90 PSI
- Sandblasters: 50–100 CFM @ 100 PSI
- Tunnel boring: 200+ CFM @ 150 PSI
A 10–15% oversizing margin accommodates multiple tools and prevents pressure drops during peak usage, ensuring consistent performance.
Case Study: High-CFM Diesel Compressors in Mining Operations
A copper mine in Arizona cut downtime by 40% after upgrading to 225 CFM diesel compressors. The units maintained 95% FAD efficiency even at 110°F, supporting six jackhammers simultaneously. This highlights the importance of aligning compressor specifications with environmental and operational extremes.
Atlas Copco’s analysis of industrial compressor operations highlights how optimizing CFM/PSI balance can reduce fuel consumption by up to 18% in heavy machinery.
Engine Power and Fuel Efficiency: Evaluating HP, kW, and Diesel vs. Alternative Power Sources
Evaluating HP and kW Ratings in Diesel Air Compressor Performance
When talking about engine performance, we usually refer to horsepower (HP) or kilowatts (kW). These measurements tell us how much power an engine produces, while brake power specifically shows what's actually available when the machine is working hard against resistance. Most industrial diesel compressors need at least 100 kW just to handle basic heavy work around factories and construction sites. Recent research from Applied Energy back in 2023 found something interesting though. When manufacturers tweak the brake thermal efficiency (BTE), they can cut down on fuel usage by roughly 12 to 18 percent in those mid-sized machines. This makes a real difference because it means engines aren't wasting as much energy matching their power output to whatever job they happen to be doing at the moment.
Energy Efficiency and Optimization Strategies for Fuel Consumption
Today's diesel compressors come equipped with variable speed drives along with tiered combustion controls that cut down on wasted fuel when sitting idle. The latest turbocharging tech really makes a difference too, getting better air to fuel mixtures which means these newer units run about 30 percent more efficiently compared to those old fixed speed models still kicking around. There's also growing interest in hydrogen diesel dual fuel systems. Early tests indicate they can slash carbon monoxide emissions by nearly four fifths without sacrificing power output. Still there are challenges though. Operators need to watch out for higher levels of nitrogen oxides coming from these systems and companies will need to invest in proper infrastructure before making the switch.
Comparative Analysis: Diesel vs. Electric and Gas Power Sources for Air Compressors
For those working in remote locations needing serious torque power, diesel engines still hold their ground. They typically produce around 20 to 40 percent more cubic feet per minute compared to similar sized gas units, plus they run longer without refueling which makes them ideal for off-grid operations. When it comes to fixed installations though, electric compressors are taking over because they cut down running expenses by about half. But there's a catch they need reliable electricity supply to work properly. Natural gas powered models sit somewhere in the middle when looking at emission reductions. The newest development worth watching is hydrogen hybrid technology which manages to boost thermal efficiency by roughly 15 to 20 percent over traditional diesel options. However, hydrogen compressors face practical challenges right now since they take up about 30 to 40 percent more room than other types for the same amount of output, making them tough to deploy in tight field conditions.
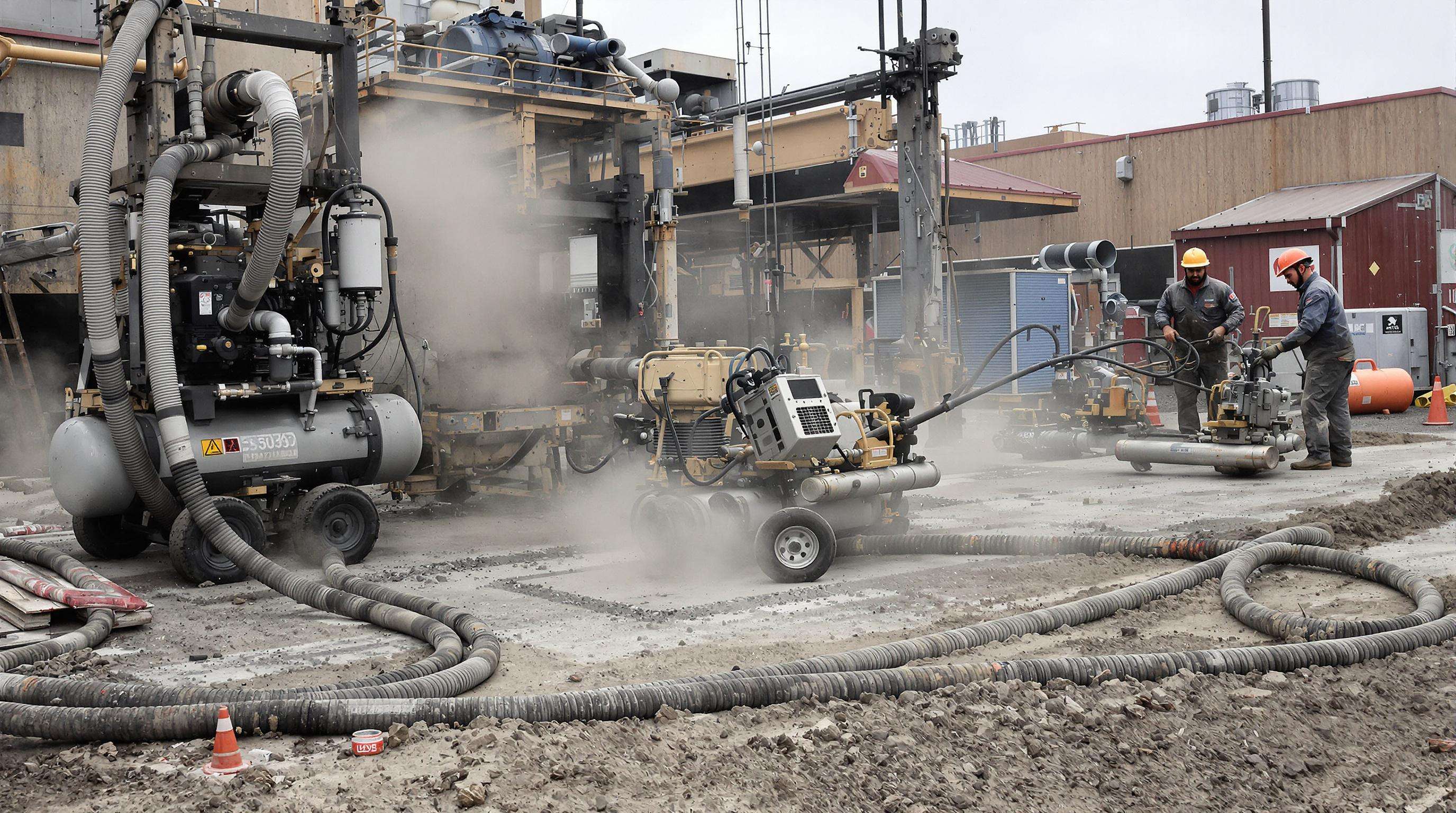
Cooling and Durability: Thermal Management and Rugged Design for Harsh Environments
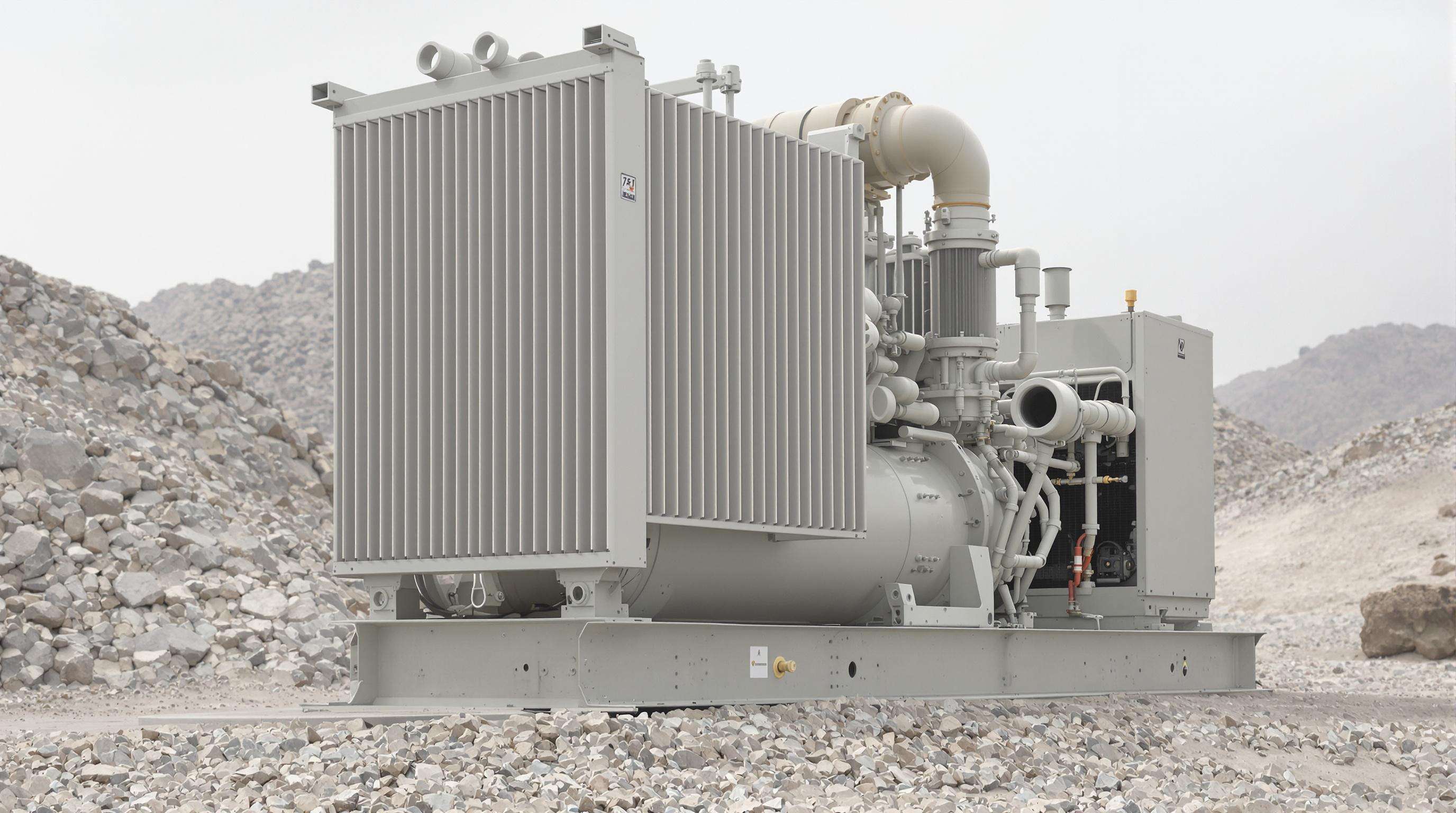

Importance of thermal management in continuous-duty diesel air compressor applications
Effective thermal management is essential for sustained performance and longevity. Overheating increases wear, reduces efficiency, and risks unplanned shutdowns. Temperature-controlled units last up to 50% longer than poorly cooled models (Heavy Equipment Journal 2023). Strategic cooling preserves component integrity and fuel efficiency, ensuring reliability in demanding operations.
Air-cooled vs. liquid-cooled systems in diesel air compressor units
Air cooled systems rely on radiators and fans to get rid of heat, which makes them pretty straightforward to maintain. These kinds of cooling solutions tend to perform best when used in vehicles or equipment that moves around a lot, especially where temperatures aren't too extreme. On the other hand, liquid cooling works differently by pumping coolant through the system, which actually transfers heat away much better than air alone can manage. That's why these systems are so popular in tough environments such as underground mining operations or desert conditions where ambient temperatures soar. The sealed nature of liquid cooling helps keep engines cooler over long periods of operation, protecting components from excessive wear even though the setup does require more parts and careful maintenance compared to simpler air cooled alternatives.
Rugged frame construction and vibration resistance
Robust engineering ensures durability in harsh conditions:
- Frame composition: High-tensile steel with optimized rigidity-to-weight ratio
- Shock absorption: Three-stage vibration isolation mounts to reduce component stress
- Component shielding: Critical parts protected by impact-resistant barriers
- Corrosion prevention: Powder-coated finishes resist chemical and humidity damage
Effective vibration damping prevents fastener fatigue and microfractures. Data from mining operations show ruggedized compressors require 40% fewer structural repairs.
Innovations in cooling efficiency for extreme environments
New technologies enhance performance in extreme temperatures. Phase-change materials absorb excess heat during operation, while smart sensors adjust fan speed dynamically. Some units feature turbulence-optimized heat-exchanging fins and aerospace-grade thermal coatings. These advancements maintain stable airflow from -20°C to 55°C, enabling reliable operation near kilns or metalworking zones.
Storage, Control, and Automation: Optimizing Output and Uptime
Role of air receiver tank size in maintaining consistent airflow
Air receiver tanks buffer demand spikes, preventing pressure fluctuations that disrupt tool performance. OSHA guidelines recommend tanks sized to hold at least 10 seconds of airflow at peak demand. Properly sized tanks reduce compressor cycling, support intermittent high-CFM tasks like sandblasting, and improve fuel efficiency.
Digital vs. mechanical control panels in modern diesel air compressor units
Digital control panels can hit around 1% accuracy when adjusting PSI or CFM settings, plus they show what's going on right away through those touchscreen displays. These are really handy for jobs that need fine tuning, think spray painting where getting the pressure just right matters a lot. Old school mechanical gauges still have their place though, especially where things get shaken up constantly like at demolition sites. The needle doesn't jump around from vibrations the way digital screens might. A lot of newer equipment actually mixes both approaches these days. They keep the mechanical system running behind the scenes as backup while letting the digital side handle most of the work. Gives operators peace of mind knowing there's something solid to fall back on if the electronics ever glitch out during critical operations.
Remote monitoring, auto-shutdown, and predictive control features
Integrated sensors monitor oil temperature, pressure anomalies, and filter status. Auto-shutdown activates at critical thresholds—such as 200°F coolant temperature—to prevent damage. Predictive algorithms analyze vibration and performance trends to forecast maintenance needs, reducing downtime by 40% and saving approximately $7,300 annually per unit in industrial fleets.
Trend: IoT integration in diesel air compressor control systems
Industrial IoT platforms now connect compressor diagnostics to centralized fleet management dashboards via encrypted 5G. Technicians receive mobile alerts for oil changes, while operators track CFM output and energy use across sites. Real-time flow monitoring enables automatic load adjustments, cutting energy costs by 22% through intelligent duty cycling.
Safety, Compliance, and Maintenance: Ensuring Reliable Diesel Air Compressor Operations
Diesel Air Compressor Specific Safety and Air Quality Considerations
Diesel compressors pose risks including carbon monoxide exposure and particulate emissions. Effective filtration systems reduce airborne contaminants by 78% in enclosed spaces (Air Quality Journal, 2023). Units should include automatic shut-off valves and pressure relief mechanisms to prevent tank ruptures during overpressure events.
Noise Reduction Technologies and OSHA Compliance
Modern units integrate mufflers and vibration-dampening frames to operate below 85 dB, meeting OSHA’s permissible exposure limits. Dual-stage air intake systems reduce noise by 30% compared to single-stage designs without sacrificing airflow efficiency.
Ventilation and Exhaust Management in Enclosed Spaces
Proper ventilation is critical when operating diesel compressors in tunnels or workshops. Best practices require 12–15 air changes per hour using dedicated exhaust ducts, with CO detectors placed within 5 meters of the unit. Cross-ventilation designs have been shown to reduce toxic fume concentrations by 92% in mining environments (Industrial Safety Review, 2024).
Maintenance Practices for Air Compressor Systems to Ensure Safety
Proactive maintenance extends equipment life by 40% and prevents 63% of compressor-related accidents (Equipment Reliability Report, 2023). Key practices include:
- Daily oil and air filter checks
- Weekly testing of safety valves and pressure switches
- Annual gasket replacement and fitting torque verification Operators must document all maintenance to comply with ASTM F2590 standards for industrial compressor safety and reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are CFM and PSI in relation to diesel air compressors?
CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute) measures the airflow an air compressor produces, while PSI (Pounds per Square Inch) indicates the pressure the air exerts. Together, they determine a compressor's capability to power pneumatic tools effectively.
Why is Free Air Delivery (FAD) important?
FAD accounts for internal inefficiencies and shows the actual output of an air compressor, which differs from theoretical CFM. Understanding FAD helps ensure equipment meets real-world operational demands.
How do diesel compressors compare to electric and gas models?
Diesel compressors offer more torque, longer run times, and better performance in remote areas, while electric compressors are cost-effective for fixed installations. Gas models provide moderate emission reductions but require reliable fuel sources.
What is the significance of thermal management in diesel compressors?
Thermal management prevents overheating, maintains efficiency, and extends compressor lifespan, particularly in continuous-duty applications within harsh environments.
How can digital control panels improve compressor operations?
Digital control panels allow precise PSI and CFM adjustments, offer real-time monitoring, and ensure better operational control. They are ideal for operations requiring fine-tuning.
Table of Contents
- Airflow and Pressure Performance: CFM, PSI, and Real-World Application Matching
- Engine Power and Fuel Efficiency: Evaluating HP, kW, and Diesel vs. Alternative Power Sources
- Cooling and Durability: Thermal Management and Rugged Design for Harsh Environments
- Storage, Control, and Automation: Optimizing Output and Uptime
- Safety, Compliance, and Maintenance: Ensuring Reliable Diesel Air Compressor Operations
- Frequently Asked Questions