Basic Principles of Air Compression
Understanding Kinetic to Potential Energy Conversion
At its core, air compression works by turning kinetic energy into potential energy. Think of it this way: when air moves, it has energy from that motion (that's kinetic energy), and air compressors grab hold of that movement and store it as something useful. The actual process involves grabbing those fast moving air molecules, squeezing them together, and keeping them packed tight as high pressure air. Basically, it takes motion and turns it into something that can be saved for later use. This whole energy conversion thing makes compressors really important for running all sorts of tools and equipment. They're found everywhere from garage workshops to big factories. Take for instance the massive compressors humming away in manufacturing facilities or the smaller ones people keep in their cars for flat tires. No matter where they are, these machines rely on the same basic principle of changing kinetic energy into stored potential energy, which is what makes them so essential across different industries.
Positive Displacement vs. Dynamic Displacement
When it comes to air compressors, there are basically two different ways they operate: positive displacement and dynamic displacement models. Let's start with positive displacement compressors. These bad boys trap air in a chamber and then squeeze that space down until the pressure goes up. We see this principle at work in reciprocating compressors with those moving pistons everyone knows about, plus the rotary screw versions that many shops prefer because they just keep running without breaking down so much. Most factories and auto repair places rely heavily on these kinds of compressors since they deliver steady pressure when needed, something critical for tasks like painting cars or operating pneumatic tools throughout the day.
Dynamic displacement compressors work differently. Take centrifugal compressors for example they boost air speed using a fast spinning impeller that turns kinetic energy into actual pressure. These kinds of compressors are great when big volumes of air are needed across varying pressure levels, which is why we see them so much in places like chemical processing facilities and building HVAC systems. Looking at what's happening in the field, most small and medium businesses stick with positive displacement models, but when operations get really large scale, dynamic compressors tend to be the better choice. Knowing how each system works makes all the difference when picking the right equipment for what the factory or plant actually needs day to day.
For more detailed insights, you can explore options like the industrial screw air compressor, offering both efficiency and reliability for industrial applications.
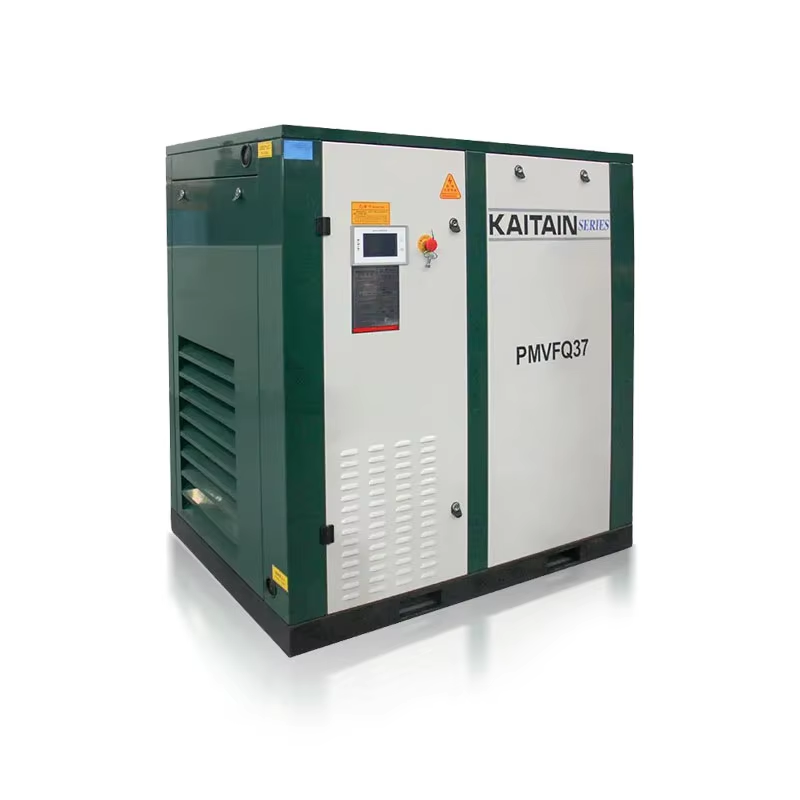
Key Components of an Air Compressor Machine
Motor/Engine and Air Intake System
At the heart of any air compressor sits either a motor or engine, which powers the whole operation using various energy sources like electricity or gas. Most folks go for electric motors because they work better and deliver steady power most of the time. Gas engines still have their place though, especially when there's no reliable electricity nearby. The air intake system plays a big role too since it pulls in outside air to start the compression going. This system includes things like intake valves, filters, and connecting parts. Good filtration matters a lot for keeping dirt and debris out of sensitive compressor components. How well the motor works makes a real difference in how good the compressor performs overall. Some research looking at factory operations showed that switching to high efficiency electric motors can cut down running costs without sacrificing performance. Getting familiar with all these parts helps explain why certain compressors work better than others in practice.
Compression Chamber and Storage Tank
Inside an air compressor, the compression chamber does most of the heavy lifting when it comes to boosting air pressure. Different models accomplish this task using either pistons or rotating parts depending on their design. For instance, reciprocating units rely on back-and-forth piston movement inside metal cylinders, whereas rotary screw versions have those long helical screws spinning continuously to keep things running smoothly. Then there's the storage tank component, sometimes referred to simply as an air receiver. This part acts basically as a holding area where all that compressed air gets stored until someone actually needs it. Getting the right tank size matters quite a bit for how well the whole system works. Bigger tanks tend to maintain better pressure levels during busy periods at factories or workshops, which helps prevent annoying drops in performance. Industry stats show that properly dimensioned storage tanks really do make a difference in keeping pressure stable across different operations. All these pieces work together pretty seamlessly in any good compressed air setup, making sure the equipment stays dependable even under tough working conditions.
Pressure Relief Valves and Gauges
Pressure relief valves play a critical role in air compressors because they release too much pressure before it causes problems. Without them, systems can fail or even become dangerous situations. These valves basically keep things under control so nobody gets hurt from unexpected bursts or explosions. Pressure gauges work differently but just as importantly. They let operators see exactly what's happening inside the system at any given moment. This visibility means technicians can spot issues early and keep everything running smoothly. Monitoring those numbers isn't just good practice either it's often required by law. Industry reports show most accidents happen when proper pressure management isn't maintained. For anyone working with compressed air systems, knowing how these components function together makes all the difference between a reliable setup and one prone to breakdowns.
The Step-by-Step Air Compression Process
Air Intake and Filtration
Getting fresh air into an air compressor matters a lot when it comes to keeping the whole system running smoothly over time. When dirty stuff gets sucked in, it doesn't just make the machine work harder but actually wears down those expensive internal parts. Most compressors rely on different kinds of filters to keep things clean inside. We typically see particulate filters grabbing dust and dirt, coalescing ones pulling out moisture, while activated carbon handles chemical smells and vapors. All these filters together protect what makes the compressor tick. Good filtration really pays off in the long run. According to research from the Journal of Industrial Maintenance back in 2020, companies that maintain their air intake systems properly saw maintenance bills drop around half and got way more life out of their equipment before needing replacements.
Compression Mechanism Variations
Air compressors come in various types, each suited to different jobs around the shop or factory floor. The positive displacement category includes rotary screws and reciprocating pistons which work great when there's a need for steady airflow over long periods. Take rotary screws for example they run pretty quietly compared to other models and tend to last longer in tough conditions. Reciprocating pistons on the other hand pack quite a punch when it comes to pressure output, so they're often seen in situations where maximum force is required. Then we have dynamic compressors such as centrifugal units that handle massive volumes of air at once, typically found in big industrial settings. According to recent studies published in the Journal of Compressor Technology back in 2021, manufacturers have made significant improvements in how efficiently these machines operate nowadays, resulting in better control and reduced energy consumption across many applications.
Storage, Cooling, and Discharge
The storage tank component in air compressors helps maintain steady pressure output throughout operation. Meanwhile, good cooling systems stop the whole unit from getting too hot and actually prolong how long the equipment lasts. Getting rid of compressed air properly matters too because it needs to flow smoothly into whatever system it's powering. Cooling is really important for this reason since it cuts down on heat buildup inside the machine, which makes everything run better overall. Research published back in 2019 by International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer found that when cooling works well, compressors tend to last around 25% longer than average. What happens if discharge isn't managed correctly? Well, pressure drops occur frequently, leading to wasted energy and reduced productivity across most industrial applications.
Applications and Benefits of Portable Air Compressors
Construction and Automotive Uses
The construction industry really depends on portable air compressors to run all sorts of pneumatic tools including nail guns, jackhammers, and those concrete vibrators that keep things moving on site. What makes them so valuable is their portability factor which saves time during setup compared to having to drag around big stationary models. When we look at automotive shops too, mechanics find portable compressors super handy for inflating tires, doing airbrush work, and handling other pneumatic jobs accurately without much fuss. Most professionals prefer going mobile rather than sticking with those bulky fixed systems. Industry data shows just how widespread this preference has become. Construction sites alone report that about seven out of ten tools actually rely on portable compressors to get the job done efficiently. Clearly, there's been a shift toward valuing mobility and getting work completed faster across different industrial settings these days.
Energy Efficiency in Small-Scale Operations
Portable air compressors save money for small operations because they run so efficiently. Manufacturers have been improving these machines over recent years with better motors and stronger materials that cut down on power usage. Most shops notice their electricity bills go down after switching to newer models. One contractor told me his shop saved around $2,500 a year just by upgrading their old compressors. These improvements make a big difference not only for pocketbooks but also for reducing environmental impact. As industries continue to rely on compressed air systems, companies are finding that investing in efficient portable compressors pays off both financially and ecologically in the long run.